Perform Hard Failover
Hard failover allows a node to be removed from a cluster reactively, because the node has become unresponsive or unstable.
Understanding Hard Failover
Hard failover drops a node from a cluster reactively, because the node has become unresponsive or unstable. It is manually or automatically initiated, and occurs after the point at which active vBuckets have been lost.
The automatic initiation of hard failover is known as automatic failover, and is configured by means of the Node Availability panel of the General settings screen of Couchbase Web Console, or by means of equivalent CLI and REST API commands. The current page explains how to initiate hard failover manually.
A complete conceptual description of failover and its variants (including hard) is provided in Failover.
Examples on This Page
The examples in the subsections below perform the same hard failover, on the same two-node cluster; using the UI, the CLI, and the REST API respectively. The examples assume:
-
A two-node cluster already exists; as at the conclusion of Join a Cluster and Rebalance.
-
The cluster has the Full Administrator username of
Administrator, and password ofpassword.
Hard Failover with the UI
Proceed as follows:
-
Access the Couchbase Web Console Servers screen, on node
10.142.181.101, by left-clicking on the Servers tab in the left-hand navigation bar. The display is as follows: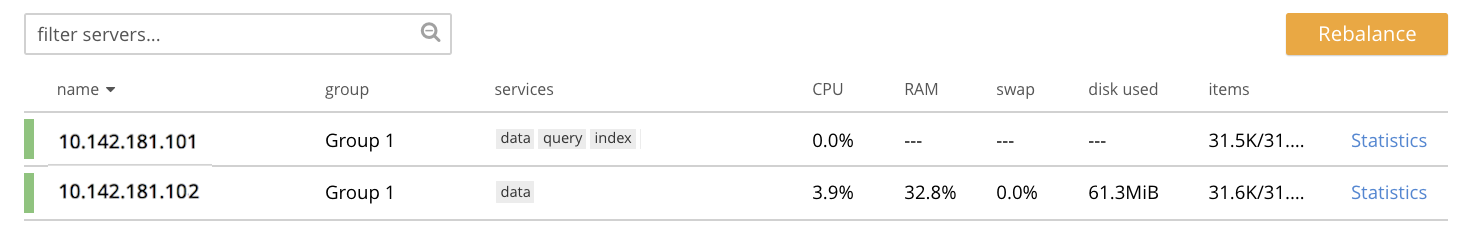
-
To see further details of the node to be failed over, which in this example will be
101.142.181.102, left-click on the row for the node. The row expands vertically, as follows: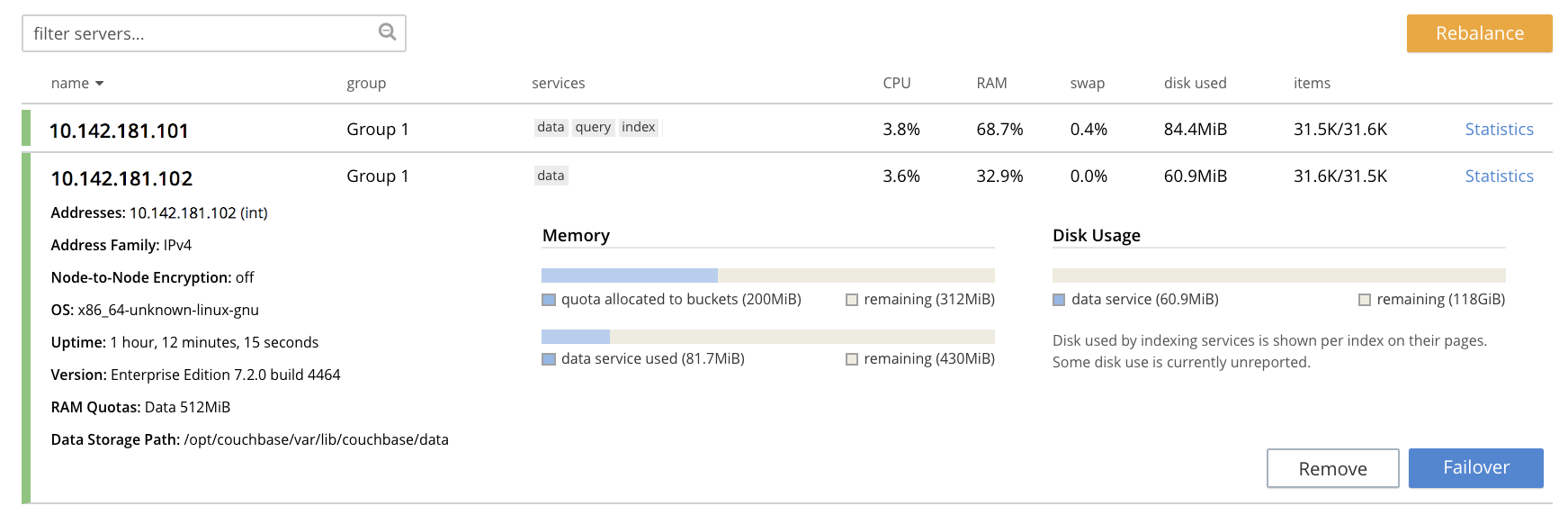
-
To initiate failover, left-click on the Failover button, at the lower right of the row for
101.142.181.102:The Confirm Failover Dialog now appears:
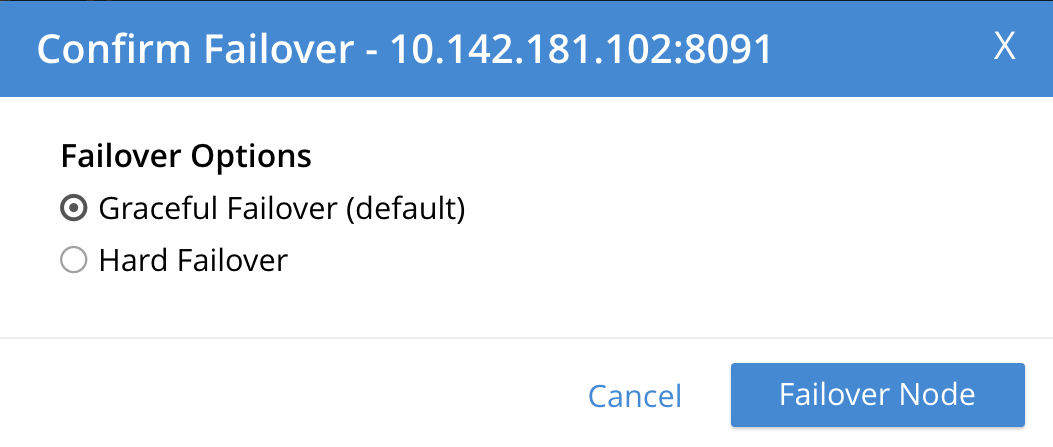
Two radio buttons are provided, to allow selection of either Graceful or Hard failover. Graceful is selected by default.
-
Select hard failover by selecting the Hard radio button:
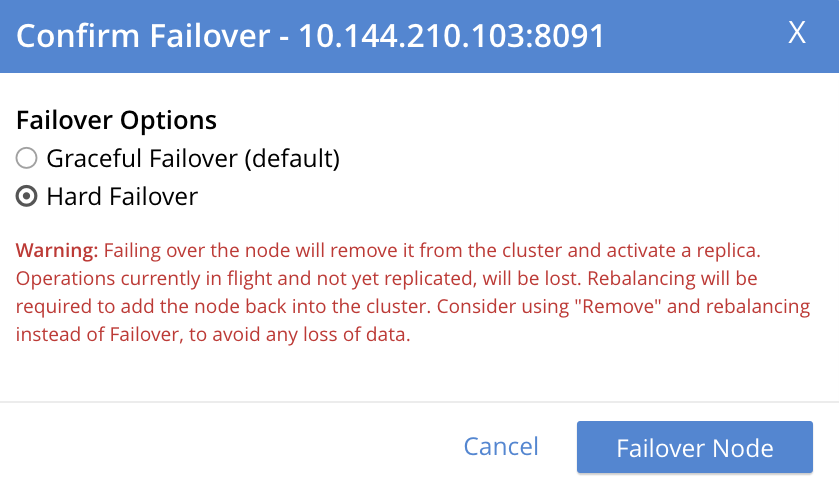
Note the warning message that appears when hard failover is selected: in particular, this points out that hard failover may interrupt ongoing writes and replications, and that therefore it may be better to Remove a Node and Rebalance, than use hard failover on a still-available Data Service node.
To continue with hard failover, confirm your choice by left-clicking on the Failover Node button.
Hard failover now occurs. On conclusion, the Servers screen appears as follows:
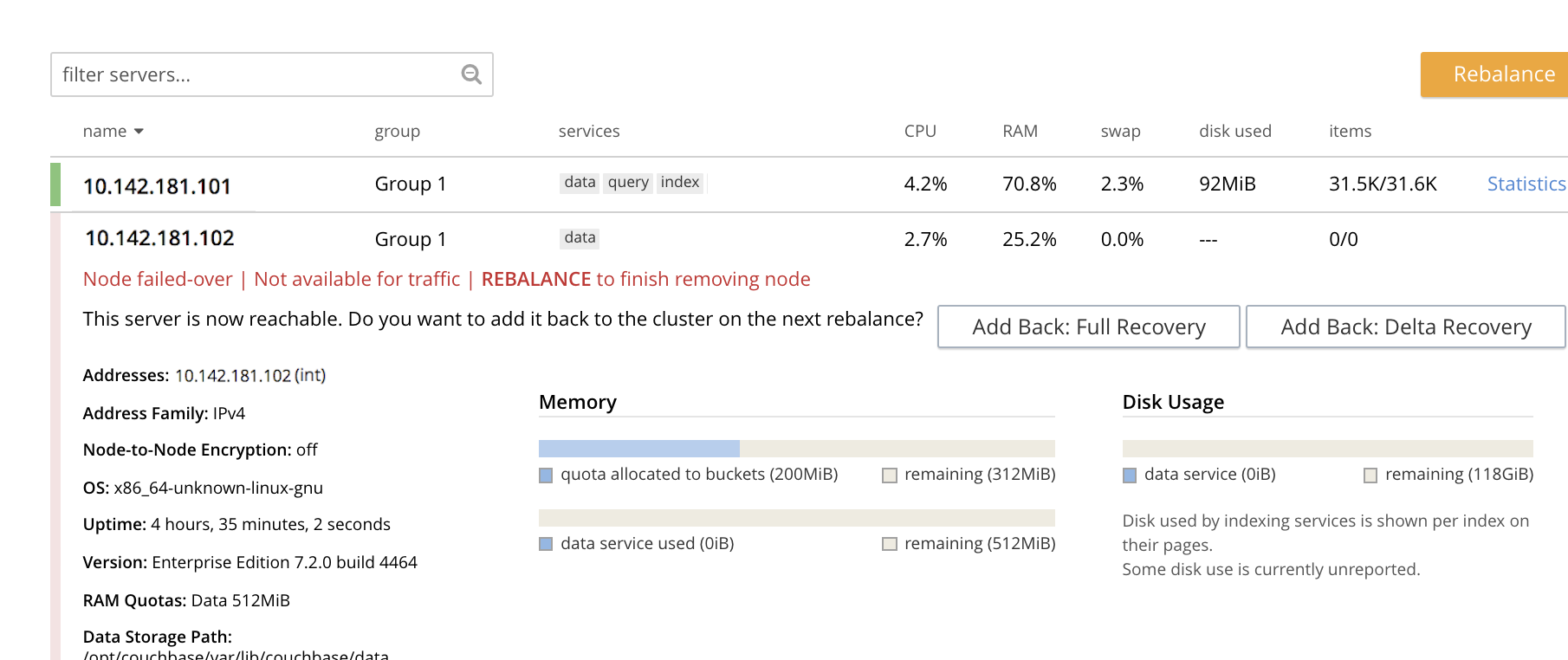
This indicates that hard failover has successfully completed, but a rebalance is required to complete the reduction of the two-node cluster to one node.
-
Left-click the Rebalance button, at the upper right, to initiate rebalance. When the process is complete, the Server screen appears as follows:

Node
10.142.181.102has successfully been removed.
Note that if rebalance fails, notifications are duly provided. These are described in Rebalance Failure Notification. See also the information provided on Automated Rebalance-Failure Handling, and the procedure for its set-up, described in Rebalance Settings.
Resetting the Auto-Failover Quota
In cases where a node has become unresponsive, and auto-failover has been configured, a button such as the following may appear, to the left of the Rebalance button:

Left-clicking on the Reset Auto-Failover Quota button causes the current count of already-occurred, successive auto-failovers to be reset to zero. Note that a rebalance, which can be started by left-clicking on the Rebalance button, also resets this count to zero, on successful completion. An overview of auto-failover is provided in Automatic Failover. Information on how to configure auto-failover is provided in Node Availability.
Hard Failover of Multiple Nodes
Hard failover of one or more nodes can be managed by means of the FAILOVER tab, toward the upper right of the Servers screen:
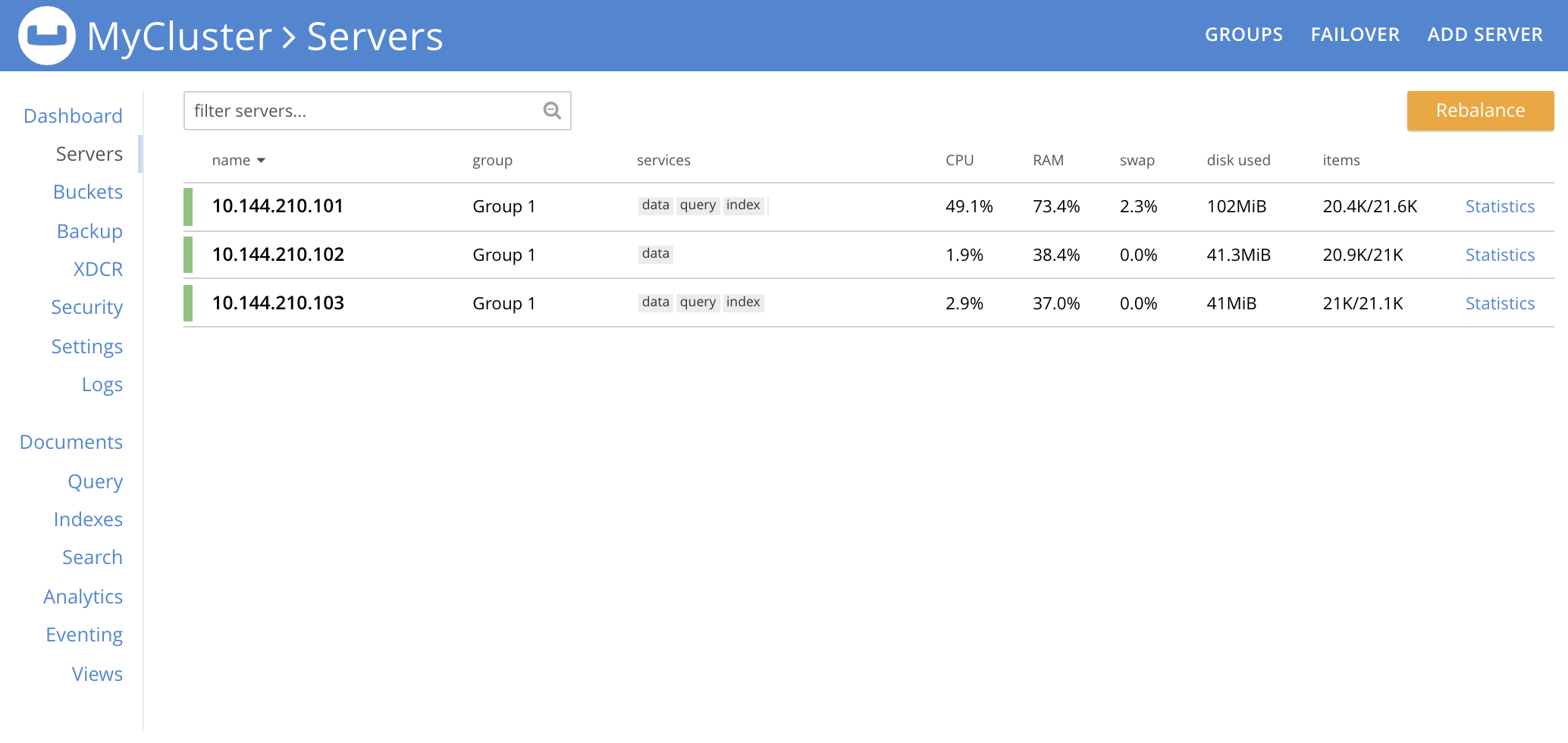
As the Servers screen here shows, this example features a cluster of three nodes. Left-click on the FAILOVER tab to perform hard failover on one or more of the three nodes:

This brings up the Failover Multiple Nodes dialog:
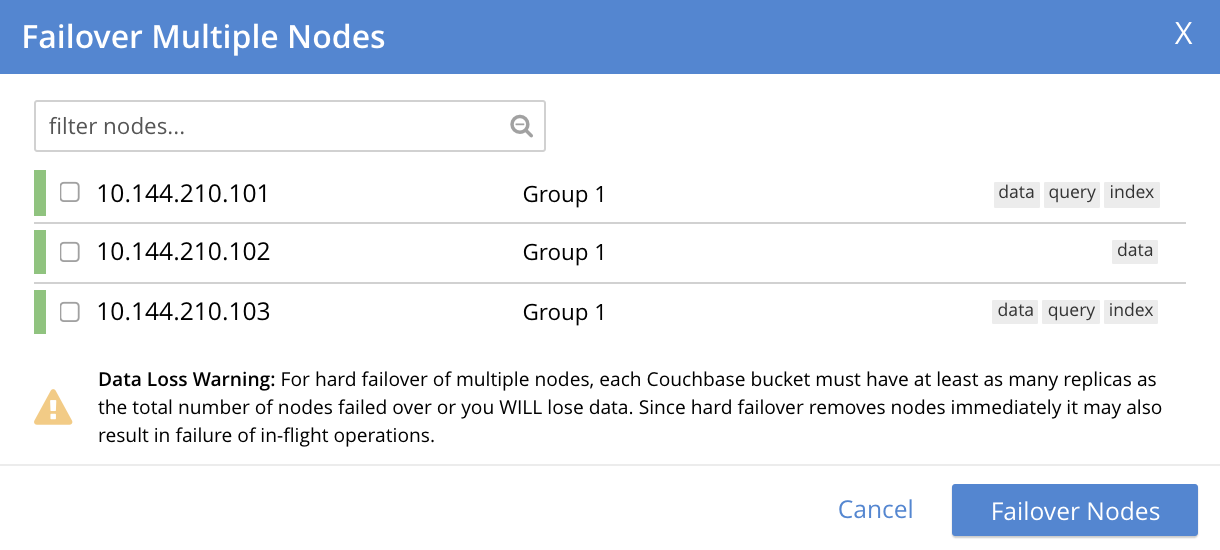
The dialog provides the following Data Loss Warning: For hard failover of multiple nodes, each Couchbase bucket must have at least as many replicas as the total number of nodes failed over or you WILL lose data. Since hard failover removes nodes immediately it may also result in failure of in-flight operations.
If you wish to perform a hard failover on multiple nodes, select those nodes from the checkboxes, then left-click on the Failover Nodes button, to start hard failover. When this has completed, a rebalance will, as usual, be required.
Hard Failover of Multiple Unresponsive Nodes
When hard failover is required due to multiple nodes being unresponsive, the Failover Multiple Nodes dialog appears as follows:
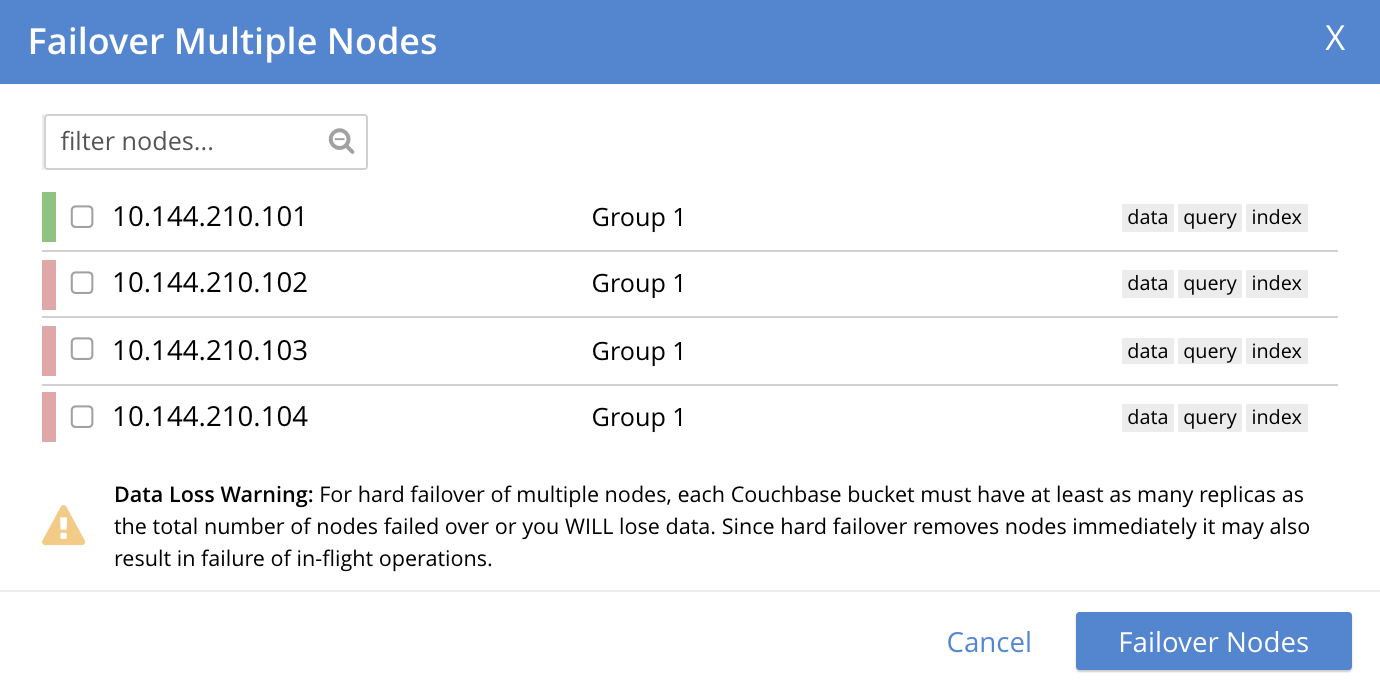
The three unresponsive nodes are those marked, at the left, with a red bar. If the checkbox for each of these nodes is selected, and the Failover Nodes button is left-clicked, the following dialog appears:
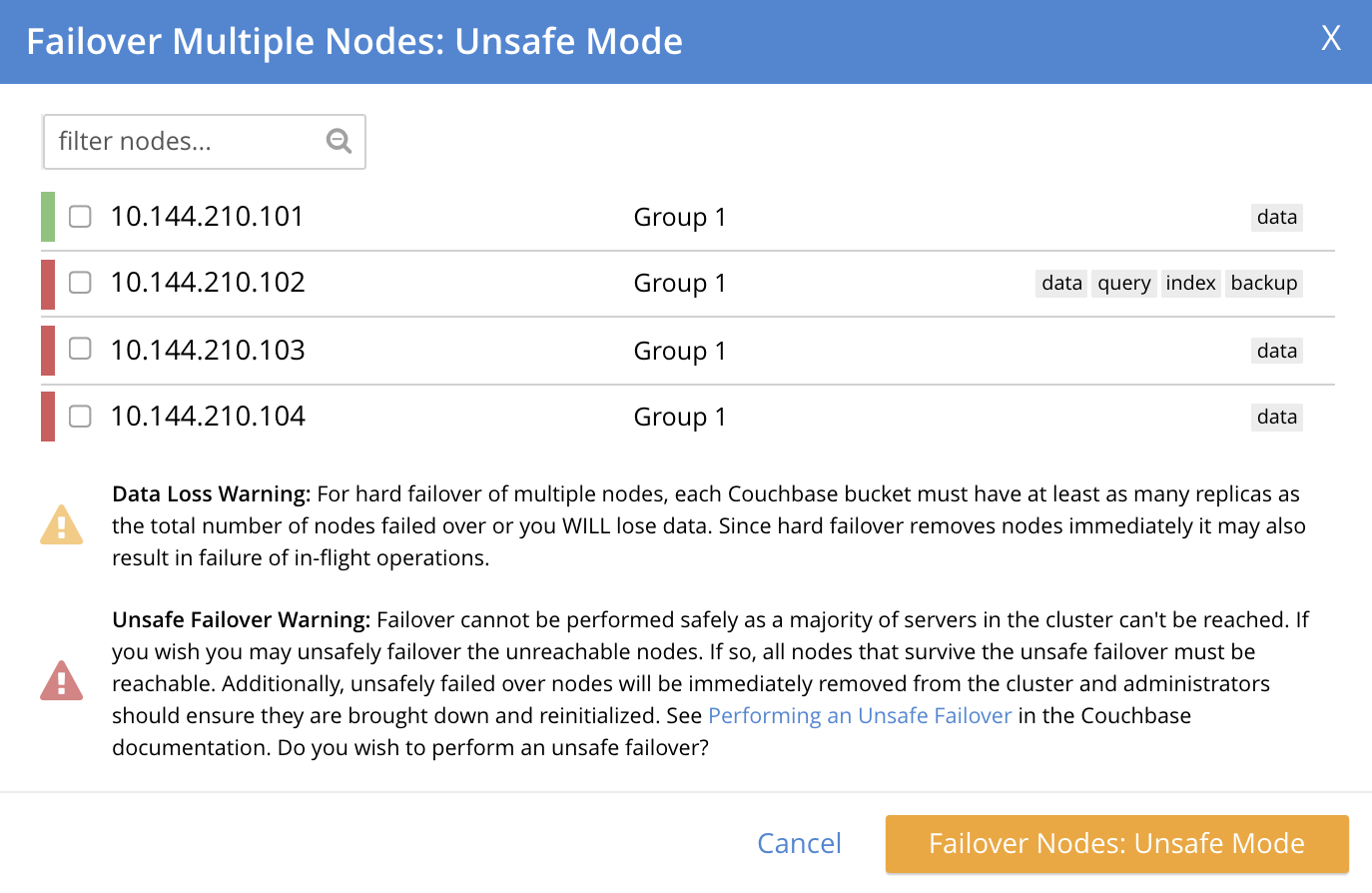
This indicates that hard failover of these nodes will be unsafe. For information on unsafe hard failover, see Performing an Unsafe Failover. If you wish to proceed, check the checkboxes again for each node to be failed over, and left-click on the Failover Nodes: Unsafe Mode button. Hard failover of the selected nodes then occurs.
Hard Failover with the CLI
To perform a hard failover on a node, use the failover command with the --hard flag.
couchbase-cli failover -c 10.142.181.102:8091 \ --username Administrator \ --password password \ --server-failover 10.142.181.102:8091 --hard
When the progress completes successfully, the following output is displayed:
SUCCESS: Server failed over
The cluster can now be rebalanced with the following command, to remove the failed-over node:
couchbase-cli rebalance -c 10.142.181.101:8091 \ --username Administrator \ --password password --server-remove 10.142.181.102:8091
Progress is displayed as console output. If successful, the operation gives the following output:
SUCCESS: Rebalance complete
In certain circumstances, an attempted hard failover will not be executed by Couchbase Server: for information, see Hard Failover in Default and Unsafe Modes.
Such an attempt therefore fails, with an ERROR: Received unexpected status 504 notification.
If hard failover must nevertheless be performed, the failover CLI expression should be re-entered: this time, with the --force flag used, in addition to the --hard flag.
This produces an unsafe hard failover.
Hard Failover with the REST API
To perform a hard failover on a node, by means of the REST API, use the /controller/failover URI, specifying the node to be failed over, as follows:
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \ http://10.142.181.101:8091/controller/failOver \ -d 'otpNode=ns_1@10.142.181.102'
Subsequently, the cluster can be rebalanced, and the failed-over node removed, with the /controller/rebalance URI:
curl -u Administrator:password -v -X POST \ http://10.142.181.101:8091/controller/rebalance \ -d 'ejectedNodes=ns_1%4010.142.181.102' \ -d 'knownNodes=ns_1%4010.142.181.101%2Cns_1%4010.142.181.102'
For more information on /controller/failover, see Failing Over Nodes.
For more information on /controller/rebalance, see Rebalancing Nodes.
In certain circumstances, an attempted hard failover will not be executed by Couchbase Server: for information, see Hard Failover in Default and Unsafe Modes.
Such an attempt therefore fails, with a Cannot safely perform a failover at the moment notification.
If hard failover must nevertheless be performed, the POST /controller/rebalance expression should be re-entered, with the same parameters as before; but this time, with the addition of the -d allowUnsafe=true parameter.
This produces an unsafe hard failover.
Next Steps
A node that has been failed over can be recovered and reintegrated into the cluster. See Recover a Node.
