Compression
Couchbase Server supports data compression in its communications with internal and external clients, and in its internal handling of items.
Overview
The compression of data allows RAM and disk-space to be used with increased efficiency. It may also reduce consumption of network bandwidth. Higher consumption of CPU resources may result.
Compression, provided by the open-source library Snappy, is applied to items based on the client’s capabilities, on the compression mode established by the user for the given bucket, and on a required minimum size for the document before compression, in relation to its size after compression (referred to as the compression ratio).
Compression is available only in Couchbase Enterprise Edition, and can be applied only to Couchbase and Ephemeral buckets. Compression applies to both binary and JSON items.
Where Compression is Used
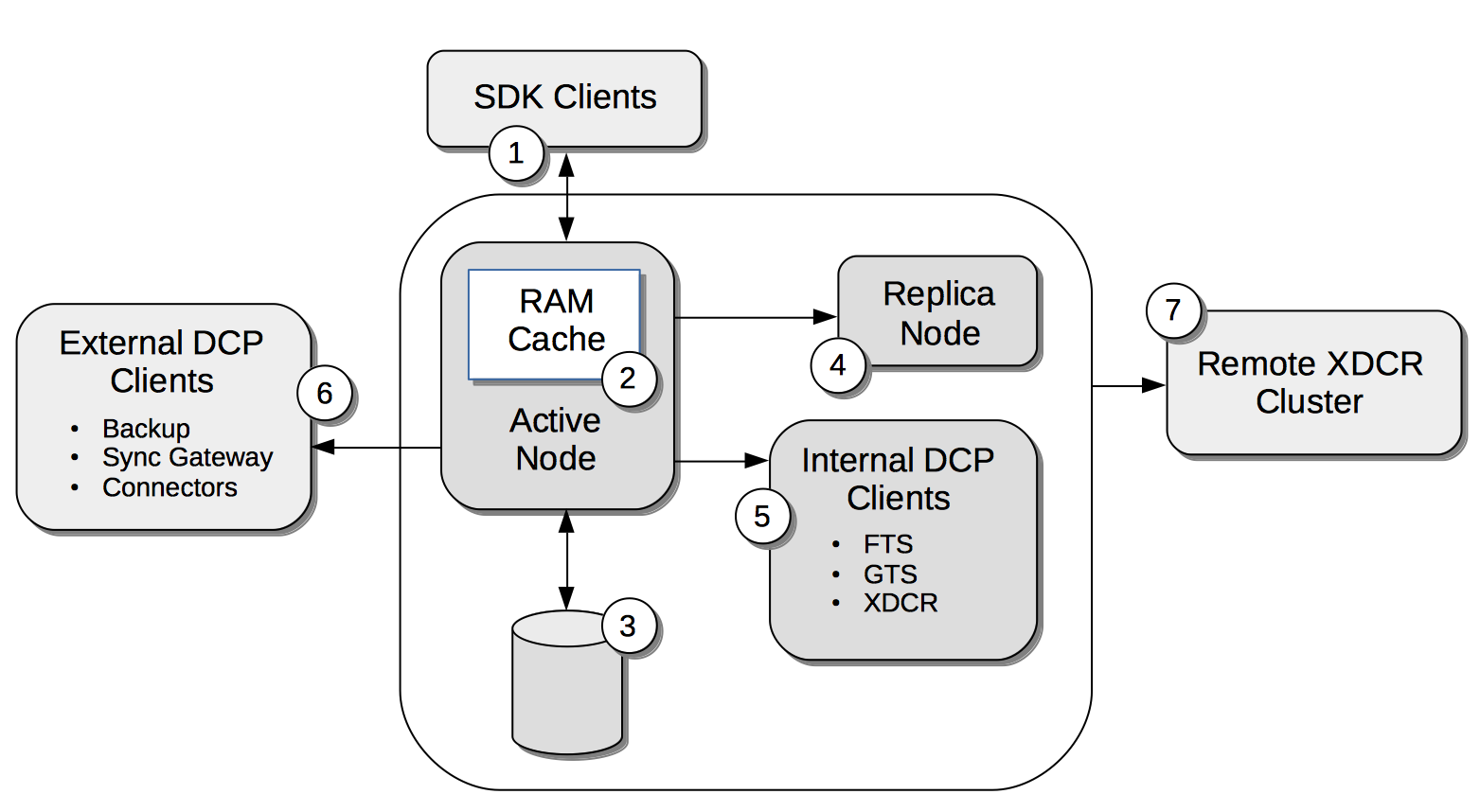
Clients based on the Couchbase SDK (1), nodes within a cluster that participate in intra-cluster replication (4), internal Couchbase Services (5), external DCP clients (6), and remote clusters that participate in Cross Data-Center Replication (7) communicate their ability to send and receive compressed items by using the HELO command, with a flag that confirms support of the Snappy Compression data type.
Couchbase Server may (depending on the mode of the bucket) store items in compressed form in memory (2). The server always compresses items when storing them on disk (3).
Compression Modes
Each bucket is configured to support one of three modes. After a client has communicated its ability to send and receive compressed data, the server’s running of compression and decompression routines depends on the mode supported by the specified bucket. The modes are as follows:
-
Off: Provides the behavior of Couchbase Server pre-5.5. On receipt of a compressed item, Couchbase Server decompresses the item when storing in memory; and recompresses it when storing on disk. Couchbase Server sends the item in uncompressed form. This mode is assigned by default to buckets upgraded from a previous version of Couchbase Server. The mode is recommended for use where clients cannot benefit from compression, and where neither memory-resources nor network-bandwidth will be negatively impacted by the size and quantity of items to be handled. Note also that this is the only mode under which Memcached buckets operate.
-
Passive: On receipt of a compressed item, Couchbase Server stores it in compressed form both in memory and on disk. Couchbase Server sends the item back to the client in compressed form if this is requested by the client; otherwise, it sends the item back in uncompressed form. On receipt of an uncompressed item, Couchbase Server stores it in memory in uncompressed form, and stores it on disk in compressed form. It returns the item to the client in uncompressed form. This mode is assigned by default to new buckets, in Couchbase Server 5.5 and beyond. It supports clients that themselves handle compression, and additionally allows Couchbase Server to limit its use of memory-resources and network-bandwidth. At the same time, it does not force Couchbase Server to use CPU resources for the compression and decompression of items that clients do not themselves require in compressed form.
-
Active: Couchbase Server actively compresses items for storage in memory and on disk, even if the items are received in uncompressed form. Items are decompressed before being sent back to those clients that do not support the receiving of compressed data. Items are sent in compressed form to clients that do support the receiving of compressed data, even if those clients originally sent the items to the server in uncompressed form. This mode allows the server to practice the maximum conservation of memory-resources and network-bandwidth. Consequently, more items can be held in memory simultaneously, and thereby accessed with improved, overall efficiency (since the processing-time required for compression and decompression is significantly less than that required for fetching data from disk). Nevertheless, in some circumstances, clients that do not themselves require the compression and decompression of items may be negatively affected by the compression and decompression performed by the server on items resident in memory.
Switching Between Compression Modes
Buckets can be switched between modes. The following behavior-changes should be noted:
-
When a bucket formerly in Passive mode has been switched to Off mode, any compressed item that Couchbase Server receives for that bucket is stored in memory in uncompressed form. If the server needs to send from the bucket an item that is currently compressed, the server decompresses the item before sending: however, to preserve memory-efficiency, the item remains compressed in memory.
-
When a bucket has been switched from Passive to Active mode, it periodically runs a task that compresses uncompressed items.
-
When a bucket formerly in Active mode is switched to Off mode, this disables the task that was periodically run to compress uncompressed items. Compressed items can continue to be received for the bucket, and are decompressed for storage in memory. Compressed items within the bucket are decompressed before sending: however, to ensure continued memory-efficiency, the item remains compressed in memory.
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is a cluster-wide parameter that specifies the minimum required size of a document before compression, in relation to its size after compression. If the document does not meet this requirement, it is retained in uncompressed form. The cluster-wide value for the parameter is 1.2.
Therefore, a document is retained in compressed form only if original_size >= (1.2 * compressed_size).
In cases where original_size < (1.2 * compressed_size), the document is retained in uncompressed form.
Enabling Compression
Couchbase Server allows authorized users to configure compression by means of the following.
-
The Couchbase Web Console, the Couchbase CLI, and the Couchbase REST API, which allow buckets each to be assigned a compression mode; and which allow Cross Data-Center Replication (XDCR) to handle compressed items.
For information on using the Couchbase Web Console to create buckets, see Create a Bucket; and for information on using it to set up XDCR, see XDCR Management Overview.
-
The
cbbackup,cbrestore, and associated tools, which allow compressed items to be requested in the backup stream. -
The Couchbase SDK, which can elect to send and receive compressed items.
For information on roles that allow modification of bucket-settings, see Authorization.