Connecting to Couchbase
How to connect to a Couchbase Cluster.
Introduction
Connecting to Couchbase can be done in several ways. This guide will take you through some of the most common methods used to access a Couchbase cluster with an SDK client or CLI tool.
A Couchbase Cluster is a combination of multiple server nodes, which can be accessed by users or applications with a username and password. Each server node can also be its own cluster or join an existing multi-node setup.
Couchbase uses Role Based Access Control (RBAC) to control access to its various services. A user or application can connect to a cluster and use these services, assuming that valid credentials with relevant access roles are provided.
Before You Begin
If you want to try out the examples in this section, follow the instructions given in Do a Quick Install to install Couchbase Server, configure a cluster, and load a sample dataset.
Couchbase Clients
Clients access data by connecting to a Couchbase cluster over the network. The most common type of client is a Couchbase SDK, which is a full programmatic API that enables applications to take the best advantage of Couchbase. This developer guide focuses on the most commonly-used SDKs, but full explanations and reference documentation for all SDKs is available.
The command line clients also provide a quick and streamlined interface for simple access and are suitable if you just want to access an item without writing any code.
|
With some editions, the command line clients are provided as part of the installation of Couchbase Server. Assuming a default installation, you can find them in the following location, depending on your operating system:
If the command line client is not provided with your installation of Couchbase Server, you must install the C SDK in order to use the command line clients. |
Read the following for further information about the clients available:
Connecting to Couchbase Server
Couchbase Server can be configured to run with unencrypted or encrypted network access. When running Couchbase in a production environment, the latter is always recommended.
Basic Auth
To connect to a standalone or Docker installation with unencrypted network access, set up a user with appropriate access levels and a secure password.
To access a cluster via the Couchbase Server Web Console over an unencrypted connection, navigate to the Web Console address with your browser (by default, localhost:8091) and enter your credentials.
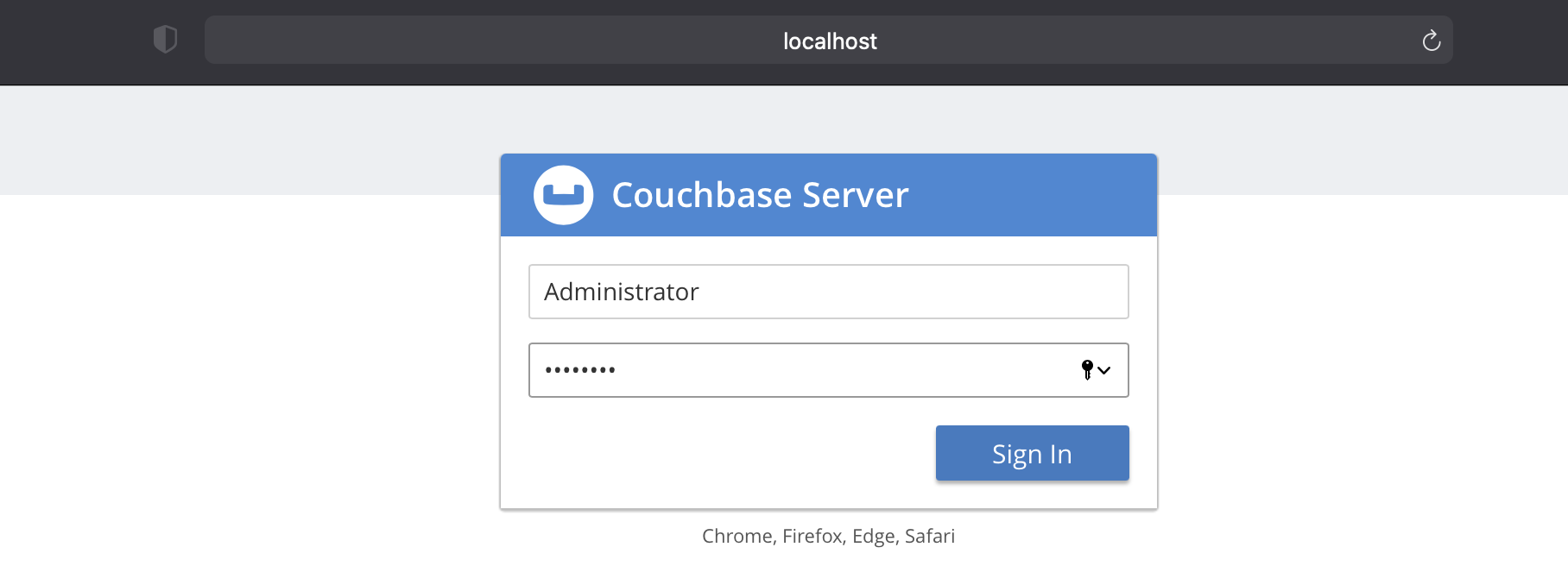
See Authenticating with the Console for more information.
Most cbc sub-commands will require some form of authentication to access a cluster or perform operations on data within a bucket.
-
To connect to Couchbase Server using
cbc, pass-ufor the username,-Pfor the password and-Ufor the connection URL immediately after a sub-command. -
Provide the bucket name required in the connection URL (i.e., couchbase://localhost/<bucket-name>).
The example below connects to the travel-sample bucket with Admin level credentials and performs a ping to check what services are running in a single-node cluster environment.
cbc ping -u Administrator -P password -U couchbase://localhost/travel-sample \
--count=1 \
--table-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| type | id | status | latency, us | remote | local |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| cbas | 0xec22b0 | ok | 3003 | localhost:8095 | 127.0.0.1:38612 |
| fts | 0xec0dc0 | ok | 3842 | localhost:8094 | 127.0.0.1:35636 |
| kv | 0xeaa220 | ok | 4446 | localhost:11210 | 127.0.0.1:49426 |
| n1ql | 0xead260 | ok | 4249 | localhost:8093 | 127.0.0.1:56740 |
| views | 0xec0430 | ok | 4045 | localhost:8092 | 127.0.0.1:60088 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
If the user credentials are invalid, cbc will return a LCB_ERR_AUTHENTICATION_FAILURE error.
|
For further details, refer to cbc(1).
Call the Cluster.ConnectAsync() method with a connection URL, username and password.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster environment with basic auth credentials.
var cluster = await Cluster.ConnectAsync("couchbase://localhost", "username", "password");
var bucket = await cluster.BucketAsync("travel-sample");
var collection = bucket.DefaultCollection();
// You can access multiple buckets using the same Cluster object.
var anotherBucket = await cluster.BucketAsync("travel-sample");
// You can access collections other than the default
// if your version of Couchbase Server supports this feature.
var customerA = bucket.Scope("customer-a");
var widgets = customerA.Collection("widgets");
// For a graceful shutdown, disconnect from the cluster when the program ends.
await cluster.DisposeAsync();Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
Call the Cluster.connect() method with a connection URL, username and password.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster environment with basic auth credentials.
Unresolved include directive in modules/guides/pages/connect.adoc - include::java-sdk:howtos:example$ManagingConnections.java[]
If the user credentials provided are invalid, the SDK will return a AuthenticationFailureException error.
|
Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
Call the connect() function with a connection URL, and a ConnectOptions object containing the username and password.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster environment with basic auth credentials.
var cluster = await couchbase.connect('couchbase://localhost', {
username: 'Administrator',
password: 'password',
})
If the user credentials provided are invalid, the SDK will return a AuthenticationFailureError error.
|
Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
-
Call the
Cluster.connect()function with a connection URL, and aClusterOptionsobject containing aPasswordAutheticator. -
Provide a username and password to the
PasswordAutheticator.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster environment with basic auth credentials.
cluster = Cluster.connect("couchbase://localhost", ClusterOptions(PasswordAuthenticator("username", "password")))
bucket = cluster.bucket("travel-sample")
collection = bucket.default_collection()
# You can access multiple buckets using the same Cluster object.
another_bucket = cluster.bucket("beer-sample")
# You can access collections other than the default
# if your version of Couchbase Server supports this feature.
customer_a = bucket.scope("customer-a")
widgets = customer_a.collection("widgets")
If the user credentials provided are invalid, the SDK will return a AuthenticationException error.
|
Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
TLS
To connect to a cluster configured with TLS (Transport Layer Security), for encrypted network access, you must supply an X.509 certificate. Before using X.509 certificate based authentication, you should run through the following:
To access a cluster via the Couchbase Server Web Console over an encrypted connection, navigate to the secure Web Console address with your browser (by default, https://localhost:18091) and enter your credentials.

See Manage Console Access for more information.
-
To securely connect to Couchbase Server using
cbc, pass-Ufor the connection URL immediately after a sub-command. -
Provide the bucket name required in the connection URL (i.e., couchbases://127.0.0.1/<bucket-name>). Note that "couchbases://" implies an encrypted connection scheme is used.
-
Pass a
certpathquery parameter to the connection URL, after the bucket name.
The example below connects to the travel-sample bucket with a client certificate, and performs a ping to check what services are running in a single-node secured cluster environment.
cbc ping -v -U "couchbases://127.0.0.1/travel-sample?certpath=ca.pem" \
--count=1 \
--tableFor further details, refer to cbc(1).
-
Call the
WithX509CertificateFactory()method on aClusterOptions()object. -
Provide the certificate store information to the
WithX509CertificateFactory()method. -
Call the
ConnectAsync()method and pass it the cluster options object.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster over a secure connection with a client certificate.
It is assumed that a valid client certificate and certificate store have been set up.
var options = new ClusterOptions().
WithX509CertificateFactory(CertificateFactory.GetCertificatesFromStore(
new CertificateStoreSearchCriteria
{
FindValue = "value",
X509FindType = X509FindType.FindBySubjectName,
StoreLocation = StoreLocation.CurrentUser,
StoreName = StoreName.CertificateAuthority
}));
var cluster = await Cluster.ConnectAsync(options);Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
-
Load a Java keystore file containing your client certificate and pass it to the
CertificateAuthenticator.fromKeyStore()method along with the required password. -
Call the
Cluster.connect()method and pass the connection string along with cluster options containing theCertificateAuthenticatorobject previously created.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster over a secure connection with a client certificate.
It is assumed that a valid client certificate and a Java keystore have been set up.
Unresolved include directive in modules/guides/pages/connect.adoc - include::java-sdk:howtos:example$Auth.java[]Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
Call the connect() function with a connection URL, and a ConnectOptions object containing a certificate trustStorePath and user credentials.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster over a secure connection with a client certificate.
It is assumed that a valid client certificate has been set up.
cluster = await couchbase.connect('couchbases://localhost', {
trustStorePath: '/path/to/ca/certificates.pem',
username: 'Administrator',
password: 'password',
})Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
-
Call the
Cluster.connect()function with a connection URL, and aClusterOptionsobject containing aPasswordAutheticator. -
Provide a username and password to the
PasswordAutheticator. -
Supply a certificate path to the
PasswordAutheticator.
The example below connects to a single-node cluster over a secure connection with a client certificate.
It is assumed that a valid client certificate has been set up.
cluster = Cluster("couchbases://localhost",ClusterOptions(PasswordAuthenticator("username","password",cert_path="/path/to/cluster.crt")))Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluser.
Connecting to Couchbase Capella
To connect to the database via Couchbase Capella, create a valid account and set up some database credentials.
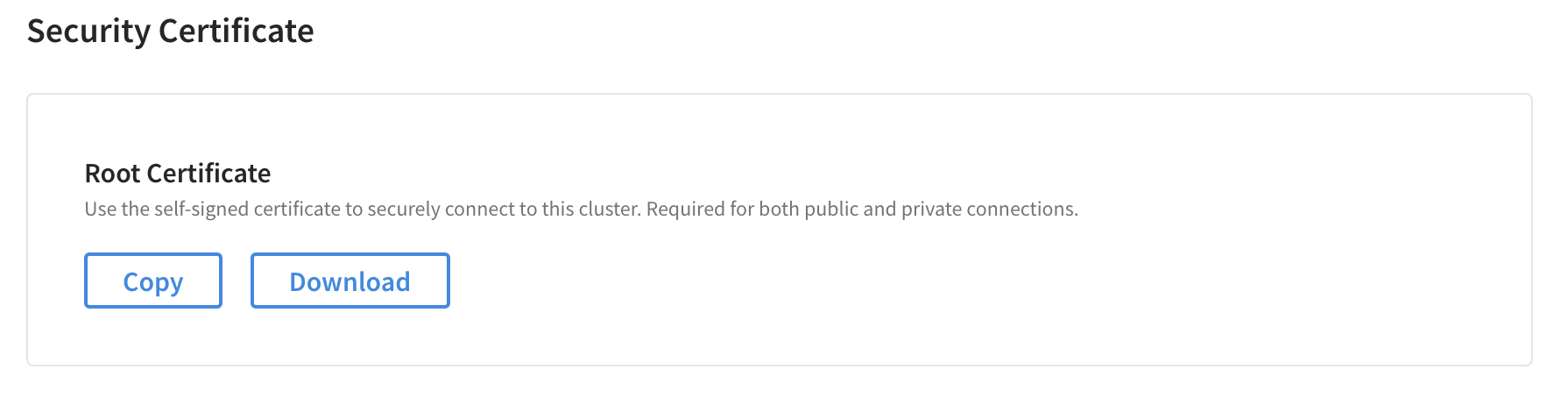
Download a security certificate to connect an SDK or CLI client to Capella.
Navigate to https://cloud.couchbase.com/login to access the Capella Web Console.
See Cluster and Data for more information.
-
To connect to Couchbase Capella using
cbc, pass-ufor the username,-Pfor the password and-Ufor the connection URL immediately after a sub-command. -
Provide the bucket name required in the connection URL (i.e., cb.<your endpoint address>.dp.cloud.couchbase.com/<bucket-name>).
The example below connects to a bucket on Couchbase Capella with a client certificate, and performs a ping to check what services are running.
cbc ping -u username -P "passworD#1" \
-U "couchbases://cb.oawlpi4audpc6jp5.cloud.couchbase.com/travel-sample?certpath=cert.pem" \
--count=1 \
--table-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| type | id | status | latency, us | remote | local |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| fts | 0x7fecf9407a70 | ok | 198657 | evb8loulphaibjnn.oawlpi4audpc6jp5.cloud.couchbase.com:18094 | 172.20.10.6:54394 |
| kv | 0x7fecfb00d110 | ok | 69737 | evb8loulphaibjnn.oawlpi4audpc6jp5.cloud.couchbase.com:11207 | 172.20.10.6:54391 |
| n1ql | 0x7fecfb0110f0 | ok | 210735 | evb8loulphaibjnn.oawlpi4audpc6jp5.cloud.couchbase.com:18093 | 172.20.10.6:54392 |
| views | 0x7fecf961e2e0 | ok | 330057 | evb8loulphaibjnn.oawlpi4audpc6jp5.cloud.couchbase.com:18092 | 172.20.10.6:54393 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------For further details, refer to cbc(1).
Call the Cluster.ConnectAsync() method with a Couchbase Capella endpoint, username, password, and client certificate.
The example below connects to a Couchbase Capella instance over a secure connection with a client certificate.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Couchbase;
using Couchbase.Query;
using Couchbase.Management.Query;
// using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
// using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
// using Serilog;
// using Serilog.Extensions.Logging;
namespace net3
{
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Update this to your cluster
var endpoint = "cb.13d1a4bc-31a8-49c6-9ade-74073df0799f.dp.cloud.couchbase.com";
var bucketName = "couchbasecloudbucket";
var username = "user";
var password = "password";
// User Input ends here.
// IServiceCollection serviceCollection = new ServiceCollection();
// serviceCollection.AddLogging(builder => builder.AddFilter(level => level >= LogLevel.Trace));
// var loggerFactory = serviceCollection.BuildServiceProvider().GetService<ILoggerFactory>();
// loggerFactory.AddFile("Logs/myapp-{Date}.txt", LogLevel.Debug);
// Initialize the Connection
var opts = new ClusterOptions().WithCredentials(username, password);
// opts = opts.WithLogging(loggerFactory);
opts.IgnoreRemoteCertificateNameMismatch = true;
var cluster = await Cluster.ConnectAsync("couchbases://"+endpoint, opts);
var bucket = await cluster.BucketAsync(bucketName);
var collection = bucket.DefaultCollection();
// Store a Document
var upsertResult = await collection.UpsertAsync("king_arthur", new {
Name = "Arthur",
Email = "kingarthur@couchbase.com",
Interests = new[] { "Holy Grail", "African Swallows" }
});
// Load the Document and print it
var getResult = await collection.GetAsync("king_arthur");
Console.WriteLine(getResult.ContentAs<dynamic>());
// Perform a N1QL Query
var queryResult = await cluster.QueryAsync<dynamic>(
String.Format("SELECT name FROM `{0}` WHERE $1 IN interests", bucketName),
new QueryOptions().Parameter("African Swallows")
);
// Print each found Row
await foreach (var row in queryResult)
{
Console.WriteLine(row);
}
}
}
}Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
Call the Cluster.connect() method method with a Couchbase Capella endpoint, username, password, and client certificate.
The example below connects to a Couchbase Capella instance over a secure connection with a client certificate.
Unresolved include directive in modules/guides/pages/connect.adoc - include::java-sdk:devguide:example$Cloud.java[]Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
Call the connect() function with a Couchbase Capella endpoint, and a ConnectOptions object containing the username, password and client certificate.
The example below connects to a Couchbase Capella instance over a secure connection with a client certificate.
var couchbase = require('couchbase')
const clusterConnStr =
'couchbases://cb.abcdefab-cdef-abcd-efab-cdefabcdef.dp.cloud.couchbase.com'
const cloudRootCertificate = '/etc/x509-cert/SSLCA/clientdir/trust.pem'
const username = 'user'
const password = 'password'
const bucketName = 'couchbasecloudbucket'
async function go() {
const cluster = await couchbase.connect(clusterConnStr, {
username: username,
password: password,
trustStorePath: cloudRootCertificate,
})
const bucket = cluster.bucket(bucketName)
const collection = bucket.defaultCollection()
// Create a N1QL Primary Index (but ignore if it exists)
await cluster
.queryIndexes()
.createPrimaryIndex(bucketName, { ignoreExists: true })
// Create and store a document
await collection.upsert('user:king_arthur', {
name: 'Arthur',
email: 'kingarthur@couchbase.com',
interests: ['Holy Grail', 'African Swallows'],
})
// Load the Document and print it
// Prints Content and Metadata of the stored Document
let getResult = await collection.get('user:king_arthur')
console.log('got: ', getResult)
// Perform a N1QL Query
let queryResult = await cluster.query(
'SELECT name FROM ' + bucketName + ' WHERE $1 in interests LIMIT 1',
{ parameters: ['African Swallows'] }
)
queryResult.rows.forEach((row) => {
console.log('query row: ', row)
})
}
go()Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.
-
Call the
Cluster.connect()function with a Couchbase Capella endpoint, and aClusterOptionsobject containing aPasswordAutheticator. -
Provide a username and password to the
PasswordAutheticator. -
Provide a client certificate path to the
PasswordAutheticator.
The example below connects to a Couchbase Capella instance over a secure connection with a client certificate.
# tag::cloud_connect[]
from couchbase.cluster import Cluster, ClusterOptions
from couchbase.cluster import PasswordAuthenticator
from couchbase.cluster import QueryOptions
# Update this to your cluster
endpoint = "--your-instance--.dp.cloud.couchbase.com"
username = "username"
password = "password"
bucket_name = "bucketname"
cert_path = "path/to/certificate"
# User Input ends here.
# Initialize the Connection
cluster = Cluster("couchbases://{}".format(endpoint), ClusterOptions(
PasswordAuthenticator(username, password, cert_path=cert_path)))
cb = cluster.bucket(bucket_name)
cb_coll = cb.default_collection()
# Create a N1QL Primary Index (but ignore if it exists)
cluster.query_indexes().create_primary_index(
bucket_name, ignore_if_exists=True)
# Store a Document
cb_coll.upsert("u:king_arthur", {
"name": "Arthur", "email": "kingarthur@couchbase.com", "interests": ["Holy Grail", "African Swallows"]})
# Load the Document and print it
print(cb_coll.get("u:king_arthur").content_as[str])
# Perform a N1QL Query
row_iter = cluster.query("SELECT cbc.* FROM {} cbc WHERE $1 IN cbc.interests".format(
bucket_name), QueryOptions(positional_parameters=["African Swallows"]))
# Print each found Row
for row in row_iter.rows():
print("Found row: {}".format(row))
# end::cloud_connect[]Click the GitHub button to view this code in context.
For further details, refer to Cluster.